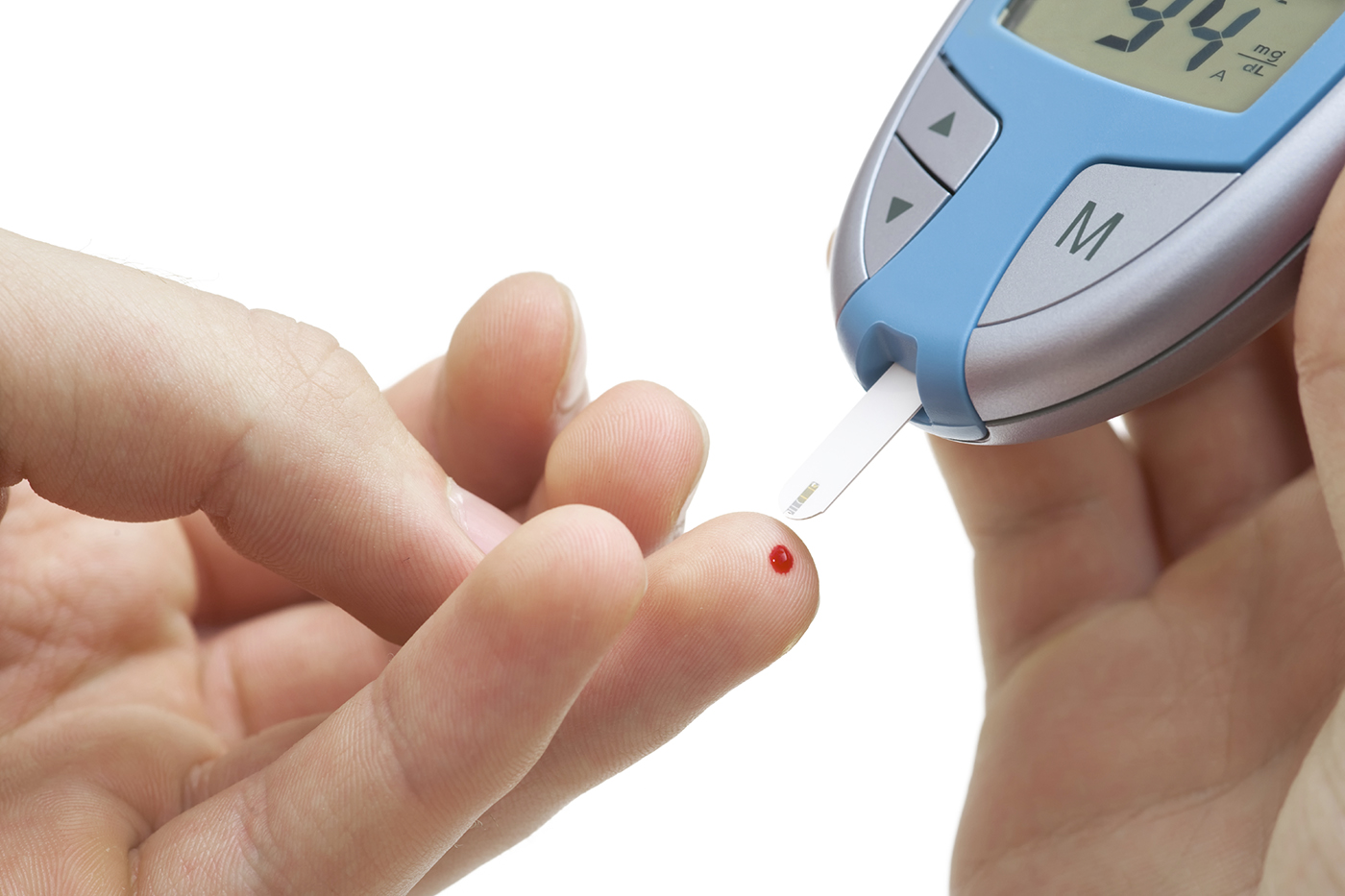
Treatment of Diabetes with Domina Pharmaceuticals:
|
Metformin Hydrochloride 500mg |
Metformin Domina 500 (Film coated tablets) |
|
Metformin Hydrochloride 750mg |
Metformin Domina 750 (Modified release tablets) |
|
Sitagliptin phosphate monohydrate 128mg |
Sitagliptin Domina (Film coated tablets) |
|
Glicalizide 80mg |
Low-Glucose 80 (Tablets) |
|
Glicalizide 30mg |
Low-Glucose 30 (Modified release tablets) |
Diabetes:
- Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces.
- Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar. Hyperglycaemia, or raised blood sugar, is a common effect of uncontrolled diabetes and over time leads to serious damage to many of the body's systems, especially the nerves and blood vessels.
- In 2014, 8.5% of adults aged 18 years and older had diabetes. In 2016, diabetes was the direct cause of 1.6 million deaths and in 2012 high blood glucose was the cause of another 2.2 million deaths.
Type 1 diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes (previously known as insulin-dependent, juvenile or childhood-onset) is characterized by deficient insulin production and requires daily administration of insulin. The cause of type 1 diabetes is not known and it is not preventable with current knowledge.
- Symptoms include excessive excretion of urine (polyuria), thirst (polydipsia), constant hunger, weight loss, vision changes, and fatigue. These symptoms may occur suddenly.
Type 2 diabetes:
- Type 2 diabetes (formerly called non-insulin-dependent, or adult-onset) results from the body’s ineffective use of insulin. Type 2 diabetes comprises the majority of people with diabetes around the world, and is largely the result of excess body weight and physical inactivity.
- Symptoms may be similar to those of type 1 diabetes, but are often less marked. As a result, the disease may be diagnosed several years after onset, once complications have already arisen.
- Until recently, this type of diabetes was seen only in adults but it is now also occurring increasingly frequently in children.
Gestational diabetes:
Gestational diabetes is hyperglycaemia with blood glucose values above normal but below those diagnostic of diabetes, occurring during pregnancy.
Women with gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of complications during pregnancy and at delivery. They and their children are also at increased risk of type 2 diabetes in the future.
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed through prenatal screening, rather than through reported symptoms.
Impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glycaemia:
Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and impaired fasting glycaemia (IFG) are intermediate conditions in the transition between normality and diabetes. People with IGT or IFG are at high risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes, although this is not inevitable.
What are common consequences of diabetes?
- Over time, diabetes can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
- Adults with diabetes have a two- to three-fold increased risk of heart attacks and strokes
- Combined with reduced blood flow, neuropathy (nerve damage) in the feet increases the chance of foot ulcers, infection and eventual need for limb amputation.
- Diabetic retinopathy is an important cause of blindness, and occurs as a result of long-term accumulated damage to the small blood vessels in the retina. 2.6% of global blindness can be attributed to diabetes
- Diabetes is among the leading causes of kidney failure
How can the burden of diabetes be reduced?
Prevention
Simple lifestyle measures have been shown to be effective in preventing or delaying the onset of type 2 diabetes. To help prevent type 2 diabetes and its complications, people should:
1- achieve and maintain healthy body weight
2- Be physically active – at least 30 minutes of regular, moderate-intensity activity on most days. More activity is required for weight control
3- Eat a healthy diet, avoiding sugar and saturated fats intake
4- Avoid tobacco use – smoking increases the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Diagnosis and treatment
Early diagnosis can be accomplished through relatively inexpensive testing of blood sugar.
Treatment of diabetes involves diet and physical activity along with lowering blood glucose and the levels of other known risk factors that damage blood vessels. Tobacco use cessation is also important to avoid complications.
Interventions that are both cost-saving and feasible in developing countries include:
blood glucose control, particularly in type 1 diabetes. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin, people with type 2 diabetes can be treated with oral medication, but may also require insulin;
blood pressure control; andfoot care.
Other cost saving interventions include:
screening and treatment for retinopathy (which causes blindness)
blood lipid control (to regulate cholesterol levels)
screening for early signs of diabetes-related kidney disease and treatment.